Different types of chillers in refrigeration industry
Chillers are simply machines that remove heat and generates cold. They are used for air conditioning and also in refrigeration industry to cool down industrial machines and factories.
You can see different types of chillers in the following diagram:
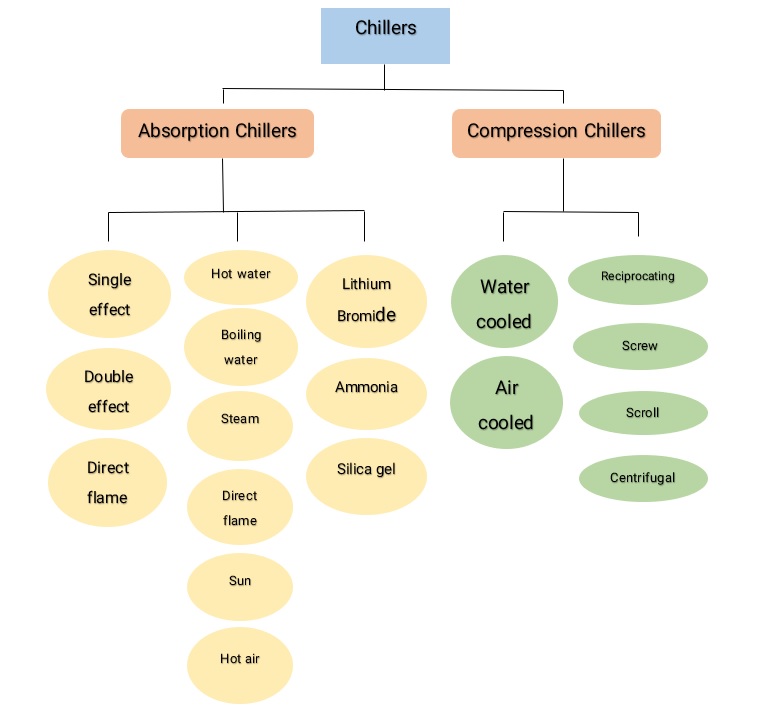
What is a compression chiller?
Compression chillers use a mechanical compressor powered by electricity to circulate refrigerant throughout the whole refrigeration system.
Compression chillers based on condenser type
There are two types of compression chillers based on their condenser type:
- Water-cooled chillers
- Air-cooled chillers
Both of these chiller types have same components: evaporator, compressor, condenser and expansion valve. We have talked about each of these components in the article named "5 main chiller components and their functions".
When we talk about air-cooled and water-cooled chillers, we are mentioning the way they remove heat out of the building using their condensers.
Air-cooled compression chillers

Air-cooled chillers use the ambient air to remove heat from the building. So, they need access to a lot of fresh air. The compressor drives the high pressure-high temperature refrigerant gas to the condenser. Refrigerant flows inside the condenser pipes and transfer its heat into the ambient air which is forced by some fans. Refrigerant losing its heat turns into liquid. So it leaves the condenser with high pressure, medium temperature and enters the expansion valve which expands the refrigerant before it enters the evaporator. The refrigerant pressure and temperature drops passing through the expansion valve. The liquid refrigerant flows over the evaporator tubes surrounded by chilled water. Heat is absorbed from the chilled water and the refrigerant evaporates. The cycle continues.
Tip: air-cooled chillers takes less space and has less maintenance cost due to their simple design but the lifespan is shorter.
Water-cooled compression chillers

Condenser in this type of chillers is cooled down using water in the cooling Tower. Four procedures are done in these machines:
- Compression by the compressor
- Condensation by the condenser
- Throttling by the expansion valve
- Evaporation by the evaporator
The cooling process is just like the air-cooled chillers. But here, when the superheated refrigerant enters the condenser, it is cooled down by the cold water from the cooling tower and turns to a high pressure liquid.
Tip: water-cooled chillers are more efficient having higher capacity but they are appropriate for using in areas with good water resources. Their maintenance cost is also higher.
Compression chillers based on compressor type
Reciprocating chillers
Reciprocating compressors use a piston and cylinder to compress the refrigerant. They are in both air-cooled and water-cooled types. They are so efficient in smaller applications for small to medium heat loads.
Screw chillers
There are two interconnecting screws inside the compressor. The refrigerant enters the void between the screws and is compressed. They are used for both water cooled and air cooled chillers and for small to medium heat loads.
Scroll chillers
The compressor contains two disks. One is stationary and the other is rotated to compress the refrigerant. It is also used for both water-cooled and air-cooled chillers but mostly on air-cooled ones.
Centrifugal compressors
This kind of compressors pressurize the refrigerant by forcing it through a rotating impeller. They are used for water-cooled chillers in medium to large heat loads.
What is an absorption chiller?

Absorption chillers use a heat source to drive the refrigerant instead of the compressor. In an absorption chiller, the generator uses a high temperature energy to turn the refrigerant into vapor. The vapor goes to the condenser and the concentrated solution returns to the absorber in which the refrigerant gas is absorbed and condenses into vapor by releasing its heat.
Absorption chillers can be categorized in three ways:
- Based on their design
- Based on their heating source
- Based on their refrigerant
Absorption chillers based on their design
Single effect chillers
These chillers have a single generator and condense all vaporized refrigerant in a single condenser
Double effect chillers
These chillers have two generators and their vaporized refrigerant from the high-temperature generator is the thermal source for the low-temperature generator.
Direct fired chillers
They are similar to single effect absorption chillers but the solution gets heated directly by the gas flame.
Absorption chillers based on the heating source
- Hot water
- Boiling water
- Steam
- Direct flame
- Hot air
Absorption chillers the based on the refrigerant
- Lithium bromide and water
- Ammonia and water
- Silica gel and water
If you watch refrigeration systems training course in HelloTechnic website, you can get more information about the chiller and their functions.


